Skilled trades research
Funding agency: Ministry of Labour, Immigration, Training and Skills Development (MLITSD)
Status: Ongoing
Project description: CISWP aims to improve the success and competitiveness of Ontario skilled-trades businesses by directly addressing workforce challenges and preventing workplace injuries and disabilities. The STRIVE OSH project consists of nine research initiatives, guided by three overarching themes: a) build capacity of the current and next generation of the skilled trades workforce; b) develop and innovate tools, guidelines, and best practices through applied research; and c) knowledge and technology exchange and exploitation. The outcomes of this work will have direct economic and societal impacts on Ontario, train the next generation of skilled trade workers in the province, and help industries (particularly small and medium-sized enterprises) build capacity and assist in promoting innovation and commercialization.

Funding agency: Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) through Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) College and Community Social Innovation Fund (CCSIF)
Status: Ongoing
Project description: Sustaining a rapidly aging workforce is a concern for Canada's construction industry, as the number of older workers is increasing faster than many other industries and construction workers experience a greater risk of injury and disability. Additionally, the risk of recurring injury amongst older construction workers is high. A promising solution to reducing injury risk are exoskeletons, which have the potential to be valuable for older workers who perform physically demanding tasks. CISWP is studying the impact of exoskeletons on worker fatigue and developing a decision-making toolkit for organizations to inform the adoption of exoskeletons.

Funding agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) College and Community Social Innovation Fund (CCSIF)
Status: Ongoing
Project description:
The skilled trades sector faces record-high job vacancy rates that will impact its economic contribution and have made skilled trades businesses less competitive. Thirteen percent of the current construction labour force is expected to retire before 2027, and the industry will need at least 170,000 workers to meet industry demand. In response, the skilled trades sector has focused on the recruitment and retention of a diverse workforce, including the participation of underrepresented groups such as women. Unfortunately, women skilled trades workers report more frequent workplace injuries and long-term disabilities compared to men, which may lead to early exits from the labour market. This applied field-to-lab-to-field research project investigates the impact of exoskeleton usage among the women skilled trades workforce and will inform the development of ergonomic guidelines for exoskeleton usage, to better support the recruitment and retention of women workers into the skilled trades.
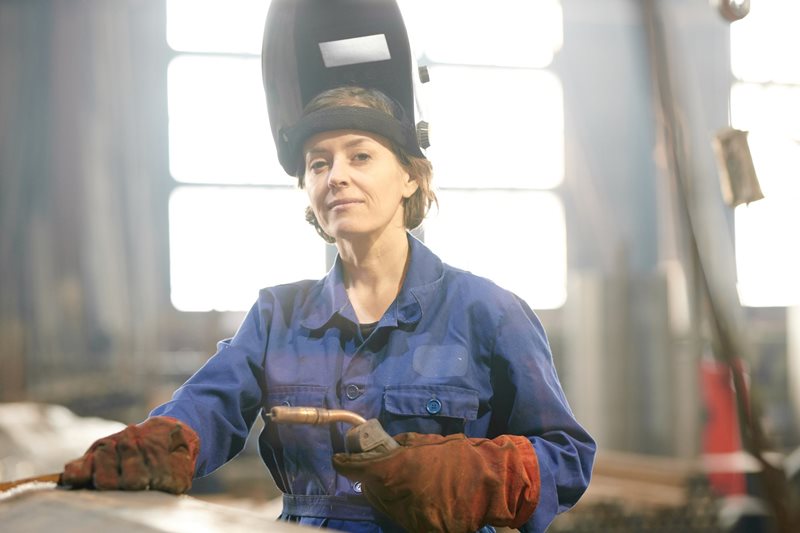

Funding agency: Workplace Safety and Insurance Board (WSIB) Research Grant Program
Status: Ongoing
Project description: Our exoskeleton manufacturing partners have intimated to us the challenges in designing their products for Canada’s diverse workforce. More specifically, there are challenges in identifying end-user needs and they do not have access to updated and relevant anthropometric (body dimension) databases representative of Canada’s large social and cultural mosaic. Ill-fitting exoskeletons may prevent equipment from functioning optimally, resulting in physiological and biomechanical burdens on workers, increase risk of workplace injury and performance deficits, create a safety hazard, and discourage its adoption and use. Using innovative 4D body anthropometric measuring equipment, this research project will lead to the development of country- and occupation- specific anthropometric databases to support the inclusive design, adoption, and implementation of exoskeletons.

Funding agency: Accessibility Standards Canada (ASC)
Status: Ongoing
Project description: There is an unprecedented opportunity to diversify the skilled trades workforce and expand it to workers that may not have had access to these careers due to diverse skills and abilities. This project focuses on the inclusion of accessible employment for people with disabilities transitioning from school to work and inform future accessibility standards for people with disabilities. Research findings may also inform strategies and practices to support the training and education of students with disabilities. Through a mixed methods approach, barriers to accessible employment will be identified, and we will understand how they can be addressed. We will elicit knowledge from the perspectives of skilled trades organizations, the lived experiences of people with disabilities, and the perspective of skilled trades trainees and apprentices who represent the future workforce.

Funding agency: Canadian Welding Bureau (CWB)
Status: Ongoing
Project description: While there is tremendous value in certification to foster innovation and as a mechanism to implement workplace injury prevention measures, the true value of certification remains largely unknown. Using primary and secondary qualitative and quantitative data, CISWP will research the impact of CWB certification on worker safety and performance and identify additional benefits such as brand recognition and reputation. By understanding the value of CWB certification, we may then be able to adopt and apply certification to its fullest potential.
Funding agency: Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and Ontario Research Fund (ORF)
Status: Ongoing
Project description: Through four interlinked research themes, CISWP addresses current and future challenges that have contributed to the significant shortage of skilled trade workers and conduct important field studies needed within the ergonomic research discipline. The funded research infrastructure consists of field measurement systems that can measure multiple dimensions of human performance and effects (e.g., physiological, biomechanical, cognitive, sensory) and multiple types of work exposures, demands, and hazards (e.g., ergonomic, psychosocial, work environment). This infrastructure will allow us to collaborate with partners to conduct innovative and highly ecologically valid applied field research with actual workers as research study participants, within real work environments, and during real working tasks.